Precision molding is the latest technology in the field of plastic injection molding. Precision molding is a type of plastic molding that is the most expensive and complex mold design process on the market.
Injection molding companies have never used the precision molding process for the entire product development process. It is only used in small, rare instances in the manufacturing process when product development requires an exceptionally precise form of plastic injection molding.
About Precision Molding
As mentioned earlier, precision injection molding is a highly technical process that requires the use of precision molds and precision machinery. The precision molding process is different from traditional injection molding technology. The process is necessary to develop precision plastic parts with complex geometries that can replace high-precision metal parts in a variety of industrial applications.
The precision of the parts depends to a large extent on the precision injection mold and its suitability to meet the engineering requirements of the design.
Related news:What Are The Requirements For Injection Molding Machines For Precision Injection Molding?
The concept of precision injection molding
Precision injection molding is a method of injection molding that is difficult to meet the requirements of injection molding machines and conventional injection molding processes. The concept of precision injection molding is mainly different from "conventional injection molding". It is based on the rapid development of polymer materials and the replacement of high-precision metal parts with precision plastic parts in the field of instruments and electronics.
At present, there are two objectives in defining precision injection molded products.
One is the repetitive accuracy of product size, and the other is the repetitive accuracy of product quality.
In this paper, we mainly describe precision injection molding from the repetitive accuracy of product dimensions. However, the precision of plastic parts cannot be equated with the precision of metal parts due to the different properties of various materials and processing processes. The mold of the molded product is an important condition to decide whether the product can meet the design requirements of precision injection molding.
Features of precision injection molding
A. High precision of parts, small tolerance, i.e. high precision dimensional limit.
B. High product requirements, requiring daily, monthly and yearly dimensional stability.
C. Good mold rigidity, high cavity size accuracy, finish and positioning accuracy between templates.
D.Adopt a precision injection molding machine instead of a conventional injection molding machine.
E. Adopt precision injection molding process.
F. Use materials that are suitable for precision injection molding.
The most important technical index for evaluating products is the precision of injection molding products (dimensional tolerance, geometric tolerance and surface finish of products). The injection molding of precision plastic products must strictly control four factors: material selection, mold design, injection molding process, and operator's technical level. Precision injection molding machine for product precision requirements within 0.01 ~ 0.001mm, many precision injection molding machines also require injection molding machine for injection pressure, injection speed requirements are high; the clamping system has sufficient rigidity and high precision clamping, the so-called clamping accuracy refers to the clamping force is uniform and adjustable, stable and repeatable high precision, the high position accuracy of the mold.
Factors affecting the accuracy of product dimensions
Mold cavity size accuracy
Accurate position of the cavity
Parting surface accuracy
The choice of material
Dimensional tolerance of general precision mold
Number of cavities in mold design
The thickness of base plate, support plate and cavity wall
Size of runner
Precision mold material (preferably alloy steel with high mechanical strength)
Design engineering
Related news:Three Questions You Need to Consider before Choosing Precision Molding
How does precision molding work?
The process of molding plastics into specially priced and calculated shapes through CNC machining is called polymer optics.
As technology grows in precision and complexity, the world requires increasingly sophisticated processes for molding plastics into specific shapes used in specialized industries such as automotive, pharmaceutical, medical device, information technology, and other service industries.
The following are some additional tips from molding consultants on the precision molding:
a. This process is beneficial because it is more economically viable.
b. The process is also a new and greatly enhanced solution to the optical problems that arise in the contract manufacturing and scientific molding of technical products.
c. The custom injection molding process is not an appropriate method for developing the optical components needed for a variety of high-precision products. The precision injection molding process allows manufacturers to customize the process to meet the needs of the molded product.
d. The resulting research and development led to Precision Injection Molding (PIM) technology, which will allow molders to develop plastic devices at an affordable price, but with very high-quality control and precision.
e. Polymer optics in precision injection molding are key to developing high precision molds, giving the plastic injection molding development process a variety of unique advantages.
f. They are ideal for molding companies to produce products in large quantities at a low cost. Prior to PIM, these products had to be developed manually by molding experts and molding consultants. Now, these products have been developed on a large scale and with a high degree of precision.
g. The integrated optical and mechanical features are unique to this product and make it superior to other custom injection molding processes.
h. Lightweight design is a key feature of custom injection molded products. Low-weight optical polymers are half the density of glass, which allows for the development of low-weight designs. Lightweight optical polymers will remain between 5-30 euros per kilogram and are much cheaper than their alternatives.
i. The process does not require any additional steps and is always done in one simple step. This means that products can be developed more accurately and in a shorter period of time through contract manufacturing.
j. The cycle time of the process is slower than that of its counterpart. The process thus becomes more suitable for the high-volume production of molded materials.
k. The process also allows production in the injection molding machine in any design or shape without any additional fees or costs.
l. Glass optics and precision optics through polymers are sometimes combined to improve the accuracy of the product, as they allow the development of high image quality control within a reasonable cost.
Automation potential
The process is highly regarded for its potential in automating the process. The entire process is automated and carried out in all aspects by computer through automated processing systems. The advanced process allows for fluid and customizable manufacturing cells.
The process of precision tooling and design engineering is carried out through cells that can also be computer programmed for injection molding, coating, testing and even packaging.
The mechanical features of the process are highly customizable, wherein mechanical mountings such as lens mounts, snaps and various other fixtures can be easily installed or removed as needed.
Surface specifications
There are limitations to the practicality of precision molding due to manufacturing technology.
Polymer optics allow lens diameters from 1 mm to 100 mm, and lens thicknesses must remain between 1 and 30 mm. The ratio of diameter to thickness will remain between 1:1 and 5:1.
Other Important Considerations
When planning to create precision molded products, it is important to consider the following key criteria.
A. Selecting the area within the mold where precision is needed
As mentioned earlier in the article, precision molding is more complex and expensive than traditional plastic molding. That's why it's important to understand the different aspects of custom plastic parts and identify parts that require high tolerances.
It is also important to know if these tolerances can be managed through traditional injection molding techniques. Plastic parts can be manufactured using traditional plastic injection molding processes as well as precision molding. For example, an electronic part may require precision machining of only a small portion of the part rather than the entire part.
Therefore, understanding and determining the accuracy requirements will ensure a cost-effective solution that meets your needs. In addition, it will help ensure that your parts are prepared with high quality and meet production deadlines.
B. Selecting the right plastic material
Choosing the right plastic resin is an important factor in making the right precision-molded part. The choice of material is one of the biggest determinants of whether a plastic molded product will be produced as desired.
Among plastic materials, shrinkage range is one of the most important criteria for manufacturing high-precision parts. A narrow shrinkage range provides a better chance of achieving tight tolerances.
Again, shrinkage requirements depend on the product being produced. While a larger range of shrinkage is not desirable because it makes it difficult to achieve the correct level of tolerance, it can still be used to make products that do not require precise dimensions.
Polypropylene has a much wider shrinkage range of +/- 0.014 in. to +/- 0.022 in. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), on the other hand, has a narrower range, but still does not fall into the category of being suitable for precision molding needs.
Typically, the shrinkage range required to mold precision parts is about +/- .001" or +/- .002"
Therefore, choosing a plastic resin with low shrinkage is an easy way to make your material suitable for precision molding.
However, due to the high cost of the required resin, this may not always be a cost-effective option.
As a result, various molders prefer to achieve high tolerance levels by adding filler materials to the plastic resin. These include glass fibers, mica and other filler materials. The addition of fillers narrows the shrinkage range and thus provides better structure to the part.
C. Choosing the best mold maker
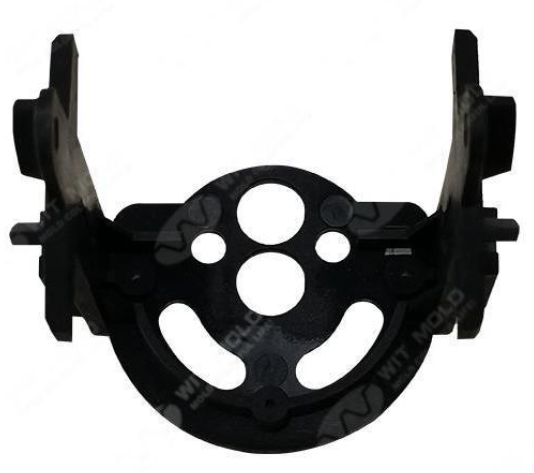
Choosing the right precision molding company is another important factor in creating quality molded products. The key requirement for manufacturing precision molded plastic parts that have tight tolerances and are produced as exact replicas of each other is having high precision molds and tooling.WIT MOLD always insists to make high quality molds.
Therefore, it is important to choose a precision mold manufacturer that is proficient in high precision tooling and has a thorough understanding of the process. The availability of technology to manufacture precision molds for the production of identical parts is a very important criterion for the manufacture of precision molded plastic products.
WIT MOLD is a very professional mould design and mould maker located South of China, certified ISO2009:2015 international quality standard. We started to build the complete molds since 2011, specializing in manufacturing different types of injection moulds for exporting worldwide mainly North America and Europe,including:
Conventional custom plastic molds
Precision injection moulds
Insert molding tools
High cavitation injection molds
Mold making for large components
Two Shot molds / 2K molds/ Bi-injection moulds
Unscrewing molds
Gas assist moulds
Injection structural foam molds
Special structural moulds
Thermoset molds
Die casting tools
We look forward to discussing cooperation with friends and business partners from all over the world.

















.png)
